Tuesday, 17 November 2015
Saturday, 14 November 2015
Best Hidden Android Secret Codes 2015
Here is list of top and best latest Best Android Secret Codes
Android device is very smart and intelligent. You find lots of secrets in android device. Here With these android secret codes you access android’s secret portal and services etc. These are the numeric/symbolic sequences which allow you to access system settings for several uses. So here we collect some Secret Hidden Codes for Android. May be some of them not work on specific device but you can try it if you can !
List of Best Android Secret Codes
An Android operating system is most widely used in the world. Android developers also creates many backdoor through which you can enter into the system and you can change settings. It is not meant to be used these backdoor for malicious intent because developers blocked some modes and these backdoor are the way or allow the users to enter into the system and let you become familiar to the system. In smartphone these backdoor are calledsecret codes. These are the numeric/symbolic sequences which allow you to access system settings for several uses. So here we collect some Secret Hidden Codes for Android. May be some of them not work on specific device but you can try it if you can.
#1 Common Android Secret Codes:
| Codes | Functioning |
|---|---|
| *#*#7780#*#* |
|
| *2767*3855# |
|
| *#*#197328640#*#* |
|
| *#*#4636#*#* |
|
| *#*#34971539#*#* |
|
| *#*#7594#*#* |
|
| *#*#273283*255*663282*#*#* |
|
| *#*#8255#*#* |
|
| *2767*4387264636* |
|
| *#0228# |
|
| *#12580*369* |
|
| *#32489# |
|
| *#273283*255*3282*# |
|
| *#3282*727336*# |
|
| *#8736364# |
|
#2 WLAN, GPS and Bluetooth Test Android Secret Codes
| Codes | Functioning |
|---|---|
*#*#526#*#*
*#*#528#*#*
*#*#232339#*#*
|
|
| *#*#232338#*#* |
|
| *#*#1472365#*#* |
|
| *#*#1575#*#* |
|
| *#*#232331#*#* |
|
| *#*#232337#*# |
|
#3 Firmware version information:
| Codes | Functioning |
|---|---|
| *#*#1111#*#* |
|
| *#*#2222#*#* |
|
| *#*#4986*2650468#*#* |
|
| *#*#1234#*#* |
|
| *#2263# |
|
| *#9090# |
|
| *#7284# |
|
| *#872564# |
|
| *#745# |
|
| *#746# |
|
| *#9900# |
|
| *#*#44336#*#* |
|
| *#03# |
|
| *#3214789# |
|
#4 Factory Tests:
| Coding | Functioning |
|---|---|
| *#*#0283#*#* |
|
| *#*#0*#*#* |
|
*#*#0673#*#*
*#*#0289#*#*
|
|
| *#*#0842#*#* |
|
| *#*#2663#*#* |
|
| *#*#2664#*#* |
|
| *#*#0588#*#* |
|
| *#*#3264#*#* |
|
| *#0782# |
|
| *#0589# |
|
| *#7353# |
|
#5 PDA and Phone:
| Codes | Functioning |
|---|---|
| *#*#7262626#*#* |
|
| *#06# |
|
| *#*#8351#*#* |
|
| *#*#8350#*#* |
|
| **05***# |
|
| *#301279# |
|
| *#7465625# |
|
#6 Other Android Secret Codes:
| Codes | Functioning |
|---|---|
| *#0*# |
|
| ##7764726 |
|
| 1809#*990# |
|
| 3845#*920# |
|
Friday, 13 November 2015
Top 6 Websites To Learn Computer Programming Languages
Top 6 Websites To Learn
Computer Programming Languages

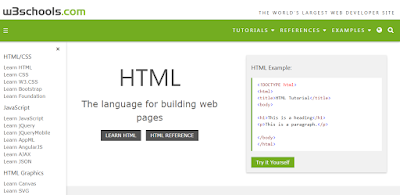
1. W3schools.com
If you are a beginner or intermediate programmer, then w3schools is an excellent website for learning programming. W3schools offer tutorials for a variety of web programming and scripting languages such as html, html5, css, asp, Ajax, JavaScript, php, jQuery etc. So, if you are into web development then w3schools would be a great learning resource.
2. Codeavengers.com:
If you want learn coding for making games, apps or websites using html/html5, css3, JavaScript python, but want an entertaining teaching resource. Then codeavengers.com is ideal choice for you. Codeavengers.com was designed by keeping difficulty for beginners in mind. It provides a fun and interactive learning environment that is effective for all age groups. Even if you are an intermediate programmer, you might find some great learning stuff there.


3. Codecademy.com
Codeacademy is another great website, for learning languages like JavaScript, HTML/CSS, PHP, Python, and Ruby. You can even learn how to use some popular web APIs in your website or app. Codeacademy has a great modern learning system, which is based on user interaction. It has full-fledged programming courses for beginners. Again, this website is great for beginners and intermediate learners. But advanced programmers can also find some pretty useful stuff there.


4. tutorialspoint.com
Tutorialspoint has tutorials for a lot of web, high level and scripting languages that are commonly used today. You can find tutorials for any computer language that you have ever heard of (those that are currently in used). Apart from that, it also features a variety of tutorials for other fields such as DIP, OS, SEO, Telecom, DBMS, and frameworks etc. Some commonly used languages that you can learn there are: Java, C++, PHP, Python, Ruby, C#, Perl, VB.Net, ios.


5. msdn.microsoft.com
Although, beginner programmers might find MSDN (Microsoft Developer Network) a tough learning resource, it is still the best resource you can get, if you want to master Microsoft oriented languages such as VB.Net, C# etc. MSDN has great tutorials for beginners, intermediate and advance programmers.

But as I stated earlier, beginners might not be initially comfortable with MDSN, as I has really a lot of resources that it would be a hard time for beginners to find what they are looking for. But if you get used to MSDN, then it is the ideal learning point for Microsoft oriented languages. You can get a lot of sample applications, tutorials and resources that are uploaded by Microsoft and MSDN community. Since it’s a developer’s network, you can even find development help from community members.
6. Lynda.com
You might already know about Lynda.com. Lynda offers easy to follow video tutorials. Lynda.com is an old and well established tutoring site, if you are looking for video tutorials to learn computer languages, then Lynda is your ideal choice. Apart from programming languages, Lynda also offers tutorials for a variety of other fields such as 3D modeling, CAD, Photography etc. Lynda.com is an old and well established tutoring site.


So the next time someone asks you about your computer skills, you know where to turn. I hope you will learn a lot from these websites. All the best :)
Thursday, 12 November 2015
Data Structures Interview Questions-Linked List
Data
Structures Interview Questions-Linked List
1. In a circular linked list
i) Components are all linked together in some sequential manner.
ii) There is no beginning and no end.
iii) Components are arranged hierarchically.
iv) Forward and backward traversal within the list is permitted.
ii) There is no beginning and no end.
iii) Components are arranged hierarchically.
iv) Forward and backward traversal within the list is permitted.
2. A linear collection of data elements where the linear node is given by means of pointer is called?
i) Linked list ii) Node list iii) Primitive list iv) None
3. Which of the following operations is performed more efficiently by doubly linked list than by singly linked list?
i) Deleting a node whose location in given
ii) Searching of an unsorted list for a given item
iii) Inverting a node after the node with given location
iv) Traversing a list to process each node
ii) Searching of an unsorted list for a given item
iii) Inverting a node after the node with given location
iv) Traversing a list to process each node
4. Consider an implementation of unsorted singly linked list. Suppose it has its representation with a head and tail pointer. Given the representation, which of the following operation can be implemented in O(1) time?
a) Insertion at the front of the linked list
b) Insertion at the end of the linked list
c) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
d) Deletion of the last node of the linked list
b) Insertion at the end of the linked list
c) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
d) Deletion of the last node of the linked list
i) a and b ii) a and c iii) a,b and c iv) I,II and IV
5. Consider an implementation of unsorted singly linked list. Suppose it has its representation with a head pointer only. Given the representation, which of the following operation can be implemented in O(1) time?
a) Insertion at the front of the linked list
b) Insertion at the end of the linked list
c) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
c) Deletion of the last node of the linked list
b) Insertion at the end of the linked list
c) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
c) Deletion of the last node of the linked list
i) a and b ii) a and c iii) a,b and c iii) a,b and d
6. Consider an implementation of unsorted doubly linked list. Suppose it has its representation with a head pointer and tail pointer. Given the representation, which of the following operation can be implemented in O(1) time?
i) Insertion at the front of the linked list
ii) Insertion at the end of the linked list
iii) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
iv) Deletion of the end node of the linked list
ii) Insertion at the end of the linked list
iii) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
iv) Deletion of the end node of the linked list
a) I and II b) I and III c) I,II and III d) I,II,III and IV
7. Consider an implementation of unsorted doubly linked list. Suppose it has its representation with a head pointer only. Given the representation, which of the following operation can be implemented in O(1) time?
i) Insertion at the front of the linked list
ii) Insertion at the end of the linked list
iii) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
iv) Deletion of the end node of the linked list
ii) Insertion at the end of the linked list
iii) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
iv) Deletion of the end node of the linked list
a) I and II b) I and III c) I,II and III d) I,II,III and IV
8. Consider an implementation of unsorted circular linked list. Suppose it has its representation with a head pointer only. Given the representation, which of the following operation can be implemented in O(1) time?
i) Insertion at the front of the linked list
ii) Insertion at the end of the linked list
iii) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
iv) Deletion of the end node of the linked list
ii) Insertion at the end of the linked list
iii) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
iv) Deletion of the end node of the linked list
a) I and II b) I and III c) I, II, III and IV d) None
9. Consider an implementation of unsorted circular doubly linked list. Suppose it has its representation with a head pointer only. Given the representation, which of the following operation can be implemented in O(1) time?
i) Insertion at the front of the linked list
ii) insertion at the end of the linked list
iii) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
iv) Deletion of the end node of the linked list
ii) insertion at the end of the linked list
iii) Deletion of the front node of the linked list
iv) Deletion of the end node of the linked list
a) I and II b) I and III c) I, II and III d) I,II,III and IV
10. In linked list each node contain minimum of two fields. One field is data field to store the data second field is?
a) Pointer to character b) Pointer to integer c) Pointer to node d) Node
11. What would be the asymptotic time complexity to add a node at the end of singly linked list, if the pointer is initially pointing to the head of the list?
a) O(1) b) O(n) c) θ (n) d) θ (1)
12. What would be the asymptotic time complexity to add an element in the linked list?
a) O(1) b) O(n) c) O(n2) d) None
13. What would be the asymptotic time complexity to find an element in the linked list?
a) O(1) b) O(n) c) O(n2) d) None
14. What would be the asymptotic time complexity to insert an element at the second position in the linked list?
a) O(1) b) O(n) c) O(n2) d) None
15. The concatenation of two list can performed in O(1) time. Which of the following variation of linked list can be used?
a) Singly linked list b) Doubly linked list c) Circular doubly linked list d) Array implementation of list
16. Consider the following definition in c programming language
struct node
{
int data;
struct node * next;
}
typedef struct node NODE;
NODE *ptr; Which of the following c code is used to create new node?
{
int data;
struct node * next;
}
typedef struct node NODE;
NODE *ptr; Which of the following c code is used to create new node?
a) ptr=(NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
b) ptr=(NODE*)malloc(NODE);
c) ptr=(NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE*));
d) ptr=(NODE)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
b) ptr=(NODE*)malloc(NODE);
c) ptr=(NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE*));
d) ptr=(NODE)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
17. A variant of linked list in which last node of the list points to the first node of the list is?
a) Singly linked list b) Doubly linked list c) Circular linked list d) Multiply linked list
18. In doubly linked lists, traversal can be performed?
a) Only in forward direction b) Only in reverse direction c) In both directions d) None
19. What kind of linked list is best to answer question like “What is the item at position n?”
a) Singly linked list b) Doubly linked list
c) Circular linked list d) Array implementation of linked list
20. A variation of linked list is circular linked list, in which the last node in the list points to first node of the list. One problem with this type of list is?
a) It waste memory space since the pointer head already points to the first node and thus the list node does not need to point to the first node.
b) It is not possible to add a node at the end of the list.
c) It is difficult to traverse the list as the pointer of the last node is now not NULL
d) All of above
b) It is not possible to add a node at the end of the list.
c) It is difficult to traverse the list as the pointer of the last node is now not NULL
d) All of above
21. A variant of the linked list in which none of the node contains NULL pointer is?
a) Singly linked list b) Doubly linked list c) Circular linked list d) None
22. In circular linked list, insertion of node requires modification of?
a) One pointer b) Two pointer c) Three pointer d) None
23. Which of the following statements about linked list data structure is/are TRUE?
a) Addition and deletion of an item to/ from the linked list require modification of the existing pointers
b) The linked list pointers do not provide an efficient way to search an item in the linked list
c) Linked list pointers always maintain the list in ascending order
d) The linked list data structure provides an efficient way to find kth element in the list
b) The linked list pointers do not provide an efficient way to search an item in the linked list
c) Linked list pointers always maintain the list in ascending order
d) The linked list data structure provides an efficient way to find kth element in the list
24. Linked lists are not suitable to for the implementation of?
a) Insertion sort b) Radix sort c) Polynomial manipulation d) Binary search
25. In worst case, the number of comparison need to search a singly linked list of length n for a given element is
a) log n b) n/2 c) log2n-1 d) n
26. consider the function f defined here:
struct item
{
int data;
struct item * next;
};
int f (struct item *p)
{
return((p==NULL) ||((p->next==NULL)||(p->data<=p->next->data) && (p->next)));
} For a given linked list p, the function f returns 1 if and only if
{
int data;
struct item * next;
};
int f (struct item *p)
{
return((p==NULL) ||((p->next==NULL)||(p->data<=p->next->data) && (p->next)));
} For a given linked list p, the function f returns 1 if and only if
a) the list is empty or has exactly one element
b) the element in the list are sorted in non-decreasing order of data value
c) the element in the list are sorted in non-increasing order of data value
d) not all element in the list have the same data value
b) the element in the list are sorted in non-decreasing order of data value
c) the element in the list are sorted in non-increasing order of data value
d) not all element in the list have the same data value
27. The following C function takes a singly linked list as input argument. It modifies the list by moving the last element to the front of the list and returns the modified list. Some part of the code left blank.
typedef struct node
{
int value;
struct node* next;
}Node;
Node* move_to_front(Node* head)
{
Node* p, *q;
if((head==NULL) || (head->next==NULL))
return head;
q=NULL;
p=head;
while(p->next != NULL)
{
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
return head;
} Choose the correct alternative to replace the blank line
{
int value;
struct node* next;
}Node;
Node* move_to_front(Node* head)
{
Node* p, *q;
if((head==NULL) || (head->next==NULL))
return head;
q=NULL;
p=head;
while(p->next != NULL)
{
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
return head;
} Choose the correct alternative to replace the blank line
a) q=NULL; p->next=head; head =p ;
b) q->next=NULL; head =p; p->next = head;
c) head=p; p->next=q; q->next=NULL;
d) q->next=NULL; p->next=head; head=p;
b) q->next=NULL; head =p; p->next = head;
c) head=p; p->next=q; q->next=NULL;
d) q->next=NULL; p->next=head; head=p;
28. The following C Function takes a singly- linked list of integers as a parameter and rearranges
the elements of the lists. The function is called with the list containing the integers 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 in the given order. What will be the contents of the list after the function completes execution?
the elements of the lists. The function is called with the list containing the integers 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 in the given order. What will be the contents of the list after the function completes execution?
struct node{
int value;
struct node* next;
};
void rearrange (struct node* list)
{
struct node *p,q;
int temp;
if (! List || ! list->next) return;
p->list; q=list->next;
while(q)
{
temp=p->value; p->value=q->value;
q->value=temp;p=q->next;
q=p?p->next:0;
}
}
int value;
struct node* next;
};
void rearrange (struct node* list)
{
struct node *p,q;
int temp;
if (! List || ! list->next) return;
p->list; q=list->next;
while(q)
{
temp=p->value; p->value=q->value;
q->value=temp;p=q->next;
q=p?p->next:0;
}
}
a) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 b) 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7 c) 1, 3, 2, 5, 4, 7, 6 d) 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)